Superhuman perception: new sensor concepts for autonomous driving
Sensing and perception are key research fields for automated driving and robotics. Research mirrors how humans sense their environment – namely with visual cues. The aim is to create superhuman perception to navigate environments shared with humans. The technology shares human-like perception strategies, augmented by additional RADAR or LiDAR sensors, with novel sensor technologies.

Machines moving among humans
As a person moves around in an environment, situational awareness achieved through visual sensing is the primary basis for decision-making. What is around me – which direction is it going and how fast is it moving?
Computer Vision will establish this situational awareness through three main research areas:
- model-driven, multi-view scene analysis or classical image analysis
- data-driven machine learning / deep learning
- system design, combining algorithms from the first two approaches
New video sensors under development offer high-resolution, high dynamic range camera systems with additional sensor information like near-infrared (NIR), depth or polarization. The multi-modal information of these sensors is fed into perception algorithms based on Deep Learning systems.
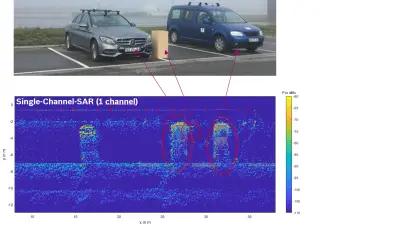
Innovative techniques such as Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) enhance radar sensors that already play a key role in current driver assistance systems. Using these techniques together with new digital modulation schemes, we can achieve superhuman resolution with a complementary physical principle. The result is radar networks enable 360-degree surround view sensing with high separability in range, velocity and angle – a milestone towards systems with superhuman perception.
Improving the sensors in cars
Simulations are an invaluable tool during development. Video and radar sensor systems can be optimized this way during development and further validate autonomous driving systems as we build them. Our research is pursuing ways to automatically generate training and validation data through simulation and image synthesis of rare driving situations. The method delivers greater confidence and efficiency as we work to solve real-world problems.
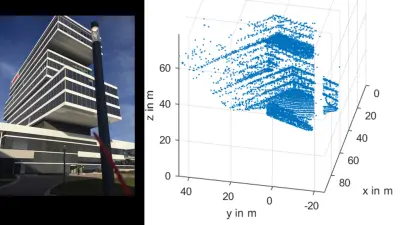
Our novel sensor concepts for LiDAR make long range and high-resolution sensors possible at low cost. We aim to demonstrate a proof of concept on our own test ground and then transfer the concept to our business unit for industrialization.
Impact on Bosch products
Video camera products such as the Bosch Multi-Purpose-Camera Gen. 3 succeed with robust real-world performance. Our system-thinking based algorithm development approach considers the constraints of series production as well as the need to implement these algorithms as HW IP blocks on the embedded computing unit of the camera. This approach differentiates Bosch Computer Vision research from purely academic research institutions.

