Mission Moon — how CubeRover™ makes autonomous docking for space possible
Bosch develops innovative solutions for extreme environments
The moon — an environment full of extremes that can push even the most advanced technologies to their limits. Abrasive dust blocks sensitive sensors, temperatures as low as -150°C challenge conventional electronics, and the complete absence of GPS makes precise navigation nearly impossible. Such conditions demand innovative solutions tailored to the unique requirements of this extraordinary environment.
Bosch brings its technological expertise to a visionary project funded by NASA’s Tipping Point program with $5.8 million. In collaboration with Astrobotic, WiBotic, the University of Washington, and NASA’s Glenn Research Center, the project unites contributions from leading innovators. CubeRover™, developed by Astrobotic, is the mission’s lightweight and modular exploration vehicle. WiBotic contributes wireless charging technology, enabling efficient energy transfer under lunar conditions. Bosch focuses on autonomous docking, providing critical systems that ensure the CubeRover™ can navigate and connect reliably in this extreme environment. The University of Washington and NASA Glenn Research Center contribute by offering performance characterization and testing of the wireless charging system.
Together, these efforts promise to revolutionize space exploration while paving the way for future innovations in autonomous systems development.
The minds behind the mission — Vivek Jain and his team
One of them is Vivek Jain, a lead expert at Bosch Research. Astrobotic serves as the principal investigator for this project, working closely with Bosch, which contributes its expertise in sensing, software, and autonomous docking for wireless power transmission.
Together, the partners are developing technologies that enable the rovers to navigate the moon with precision — without GPS. To achieve this, Bosch relies on a combination of camera data, Wi-Fi fingerprinting and sensor fusion. These approaches ensure that the rovers operate reliably even under extreme conditions such as intense light or presence of sticky lunar dust. With these innovative solutions, Bosch plays a crucial role in advancing the development of autonomous systems designed for the moon's demanding environment.

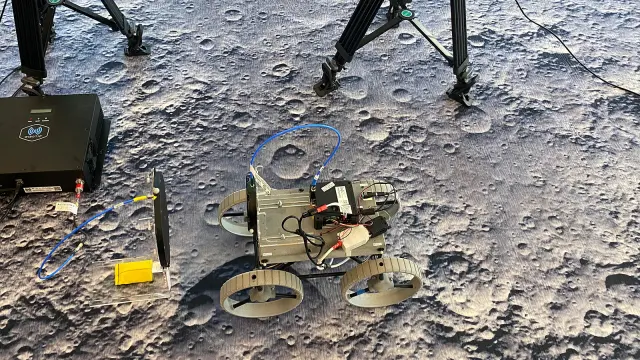
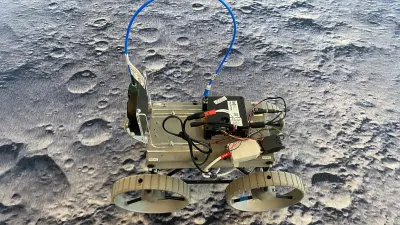
CubeRover™ — small, lightweight, and efficient
CubeRover™ is the centerpiece of the lunar mission, designed specifically for operation on the moon’s surface. A modular, ultra-lightweight, and compact rover, its smallest form factor weighs less than 5 pounds and is roughly the size of a shoebox. These characteristics enable the simultaneous transport of multiple rovers on a central platform (lander), which lands on the lunar surface and serves as a base station for power and navigation.

This makes missions not only more flexible but also more cost-effective, as multiple rovers can be deployed with a single launch. In addition to its compact size, CubeRover™ impresses with its versatility. It can carry scientific instruments such as cameras or spectrometers, opening up new approaches to lunar exploration. With its innovative technology and ability to operate reliably even in extreme environments, it represents a turning point in the exploration of new worlds.
Reaching the destination without GPS — the challenges of navigating the moon
How Bosch develops creative solutions for navigation.